Rapid coronavirus test speeds up access to urgent care
Cambridge university researchers have analysed the impact of using point-of-care testing at Addenbrooke's hospital.
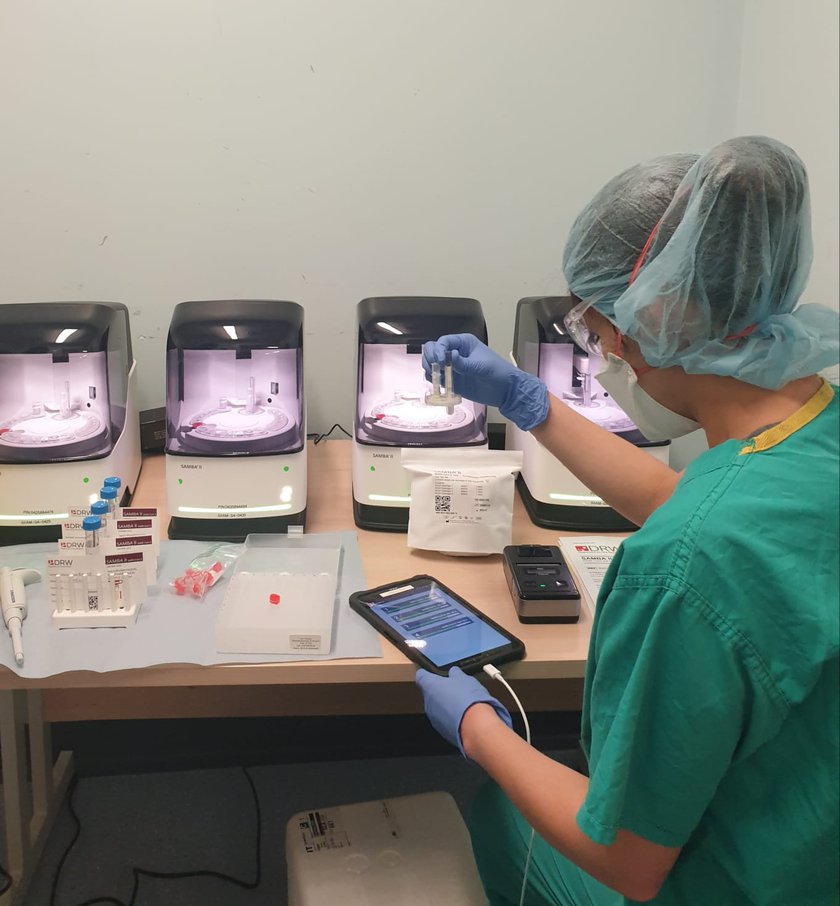 Rapid coronavirus test speeds up access to urgent care and will free up beds ahead of winter
Rapid coronavirus test speeds up access to urgent care and will free up beds ahead of winter
-
The SAMBA II diagnostic device cuts COVID-19 test result times from over 24 hours to just two hours.
-
First study of SAMBA devices on hospital wards finds patient time on COVID ‘holding wards’ was almost halved.
-
Researchers say faster tests helped free up beds and expedite access to life-saving treatments such as organ transplants – and might make all the difference later this year.
The first analysis of a new point-of-care “nucleic acid test” for SARS-CoV-2 in a UK hospital setting shows these machines dramatically reduce time spent on COVID-19 ‘holding’ wards – allowing patients to be treated or discharged far quicker than with current lab testing set-ups.
The rapid diagnostic capability of SAMBA II devices – an average of 2.6 hours compared with 26.4 hours for standard lab tests – led to an increased availability of ‘isolation rooms’ needed for infected patients, as well as fewer hospital bay closures.
University of Cambridge researchers behind the new study, currently a pre-print and awaiting peer-review, say that the time and hospital capacity spared by these devices will be “critical as we move towards autumn and winter”.
The SAMBA II machine was developed by a University spinout company, Diagnostics in the Real World, and deployed for trials in Addenbrooke’s Hospital, part of Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust (CUH).
For more information visit: CUH News
Published June 3, 2020
Latest from CCTU
Targeting the immune system could prevent future heart attacks, Cambridge-led trial suggests
Cambridge researchers have discovered that an existing therapy which boosts protective immune cells in people who have recently had heart attacks reduces…
Cambridge study finds hot flush treatment has anti-breast cancer activity
A drug mimicking the hormone progesterone has anti-cancer activity when used together with conventional anti-oestrogen treatment for women with breast…
Innovative trial offers hope on World Pancreatic Cancer Day
An early-stage trial, recently opened at Addenbrooke's Hospital, offers new hope to people with late-stage pancreatic cancer and their families.
…






